How Did Loyalty to the City States Divide Greece
Why was ancient greece divided into a collection of city-states. How did loyalty to the city-states divide greece.

Hellenistic Greece Ancient Greece Timeline Definition History
545 BCE to 448 BCE.

. City states came about in Greece mainly because of its physical characteristics. I am a man of Sparta Or. Also slaves are an important part of our city-states functionality.
Check for Understanding List three ways Greek city-states created the idea of citizenship. Which body of the Greek government included all the citizens who. They traded with each other.
I am a man of Athens He would name his home city-state. Also each city-state worshiped a god or a goddess. The ancient Greeks were very loyal to their city-state.
1 Get Other questions on the subject. Essentially the city-states had humble beginnings and started some time after the Greek Dark Ages. As a result city-states wouldonly fight or mobilize in cases where the individual.
CIts flat plains covered too much territory to allow for easy communication between cities. However strong loyalty to their individual city-states also divided Greece. The acropolis also served as a religious center where temples and alters were built to honor their many gods and goddesses.
All of the above e. The agora served as a market place and a meeting place. Individuals could move freely from one city-state to another.
They negotiated with each other. How did loyalty to the city-states divide Greece. It was relatively rare for an outsider like the Persians or Carthaginians to come under conflict with a Greek City States in their 900 years between 1200 BC and 340 BC with the Rise of Macedon.
How did loyalty to the city-states divide. A polis is an independent city or state that. Some of the city- states were oligarchiesruled by the powerful elite members of society.
Strong loyalty to their individual city-states also divided Greece. When they did they generally found that the Greeks with all their experience fighting each other did well against foreign invaders. How did establishing new colonies affect Greek industry.
For example Spartas deity was Athena the goddess of wisdom. Which type of social group commands a members esteem and loyalty. Characteristics of the city in a polis were outer walls for protection as well as a public space that included temples and government buildings.
They competed with each other. Its many islands high mountains and remote peninsulas isolated population centers. Persia Makes War Against the Greek City-States.
As a result city-states would only fight or. In Athenian democracy people voted for the laws that they wanted. Loyalty to their city-state.
Check for Understanding List three ways Greek city-states created the idea of citizenship. Inland communities were separated from each other by rugged mountains and deep valleys. In a citizens elect the president as head of government separately from the legislature.
A Greek citizens loyalty was directed to his city-state. The loyalty to the city-states was greater than the loyalty toany larger conception of Greece. The temples and government buildings were often built on the top of a.
Athens had a very special kind of government called democracy which meant rule of the people. Up to 24 cash back The polis gave Greek citizens a sense of belonging. None of the above 6.
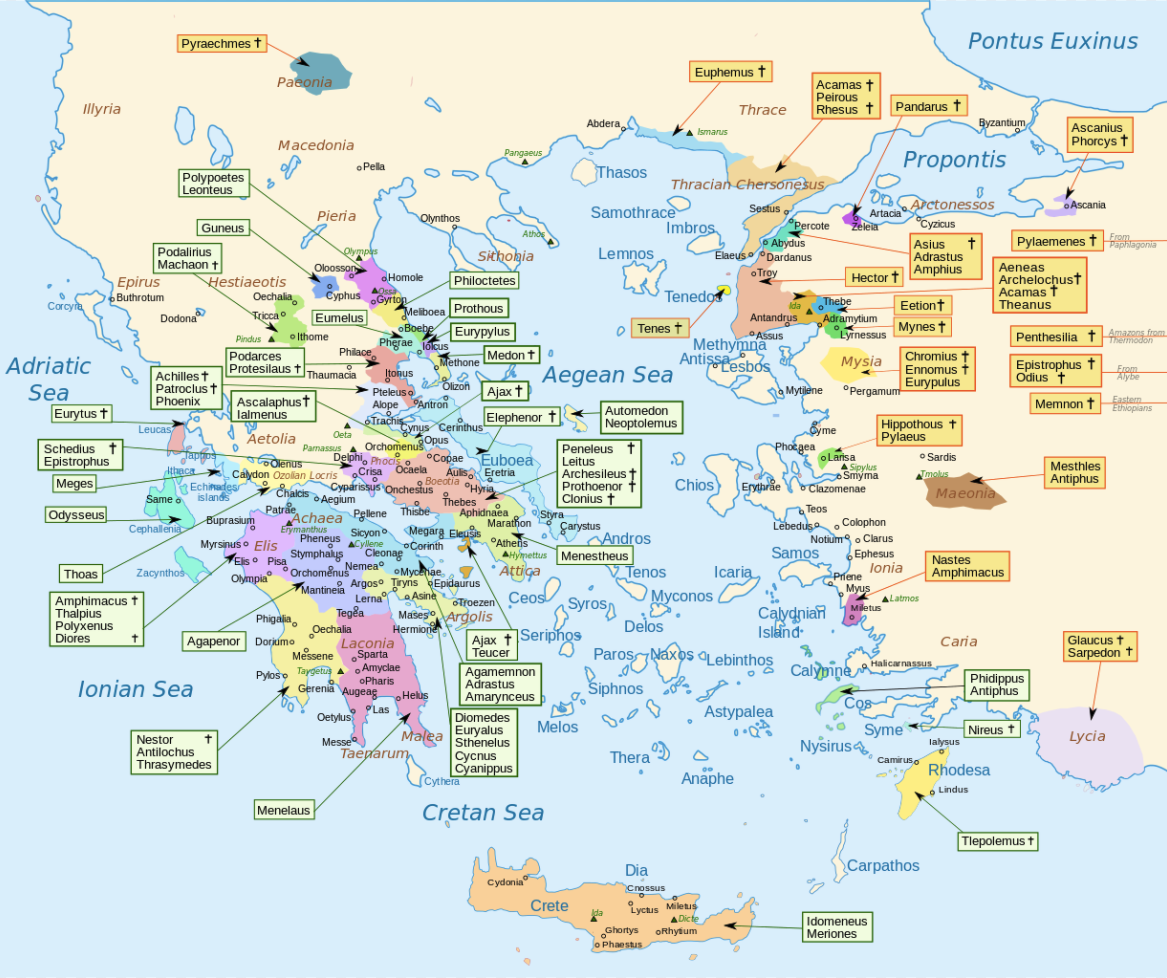
What type of government did the city-states of Greece have. Collectively the city-states of ancient Greece qualify as a civilization - a very great civilization. Greek city-states were known as a polis.
One major reason why ancient Greece was dominated by small city-states and independent towns rather than by one all-powerful king is its geography. Beginning in the mid-6th century BCE Persia arriving from the east makes trouble for the city-states through a series of sorties and full-scale wars. Many Greek communities were not near the sea.
These city-states often made alliances with other cities forming into leagues confederations or federations while maintaining an independent identity. How did seas influence the way many ancient Greeks lived. Men who were born in the city of Athens d.
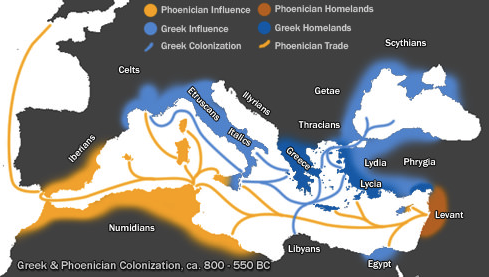
When the very rocky landscape around a city no longer supported the growing population they sent people to start colonies in other areas along the Mediterranean. Social Studies 22062019 0930 priscilaannmendez. Its mountainous terrain caused the population to spread out and create separate city states.
This lack of unity weakened Greece and made it easier for outsiders to conquer Greece. The loyalty to the city-states was greater than the loyalty to any larger conception of Greece. How did loyalty to the city-states divide Greece.
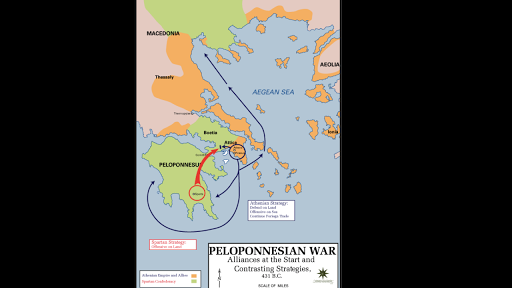
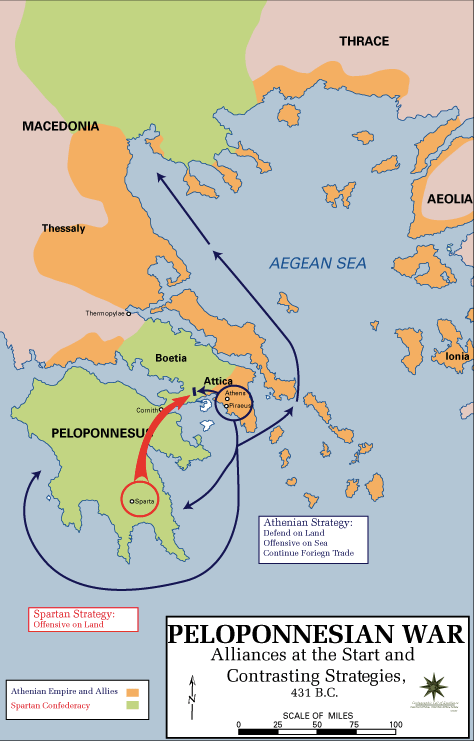
Did they get along with each other. If you were to ask an ancient Greek man where he was from he would not say Im from Greece. To resist the Persians the strongest two city-states Sparta and Athens maintain a fragile alliance.
This lack of unity weakened Greece and made it easier for outsiders to conquer Greece. As each area grew in population they eventually organized into larger cities referred to as poleis or. As a result the communities were fiercely independent and thought of themselves as separate countries.
Anyone who professed their loyalty to Athens e. In a confucian culture loyalty of the subordinates to their superiors should be. The acropolis was the main gathering place.
City-states went to war with each other. They teamed up to fight another Greek city-state or to fight a common enemy from outside the Greek peninsula. Up to 24 cash back For government both city-states have a democracy that includes a council of 500 men who discuss the problems of their everyday life.
Most of the city-states were monarchiesruled by a king. Why was it so important for a knight to take a vow of loyalty to his lord. They are an important part of the city-states archery division and also did work in fields gathering crops or mining.
A city-state or polis was the community structure of ancient GreeceEach city-state was organized with an urban center and the surrounding countryside. Because Greece didnt have many vital resources they were forced. How did loyalty to the city-states divide greece.
All men and women over the age of 13 5. Aits citizens wanted direct democracy which required smaller more manageable social units.

Decline And Fall Of Greece History For Kids
The Greek Polis Article Classical Greece Khan Academy

Battle Of Marathon Definition Facts Who Won History

Hellenistic Greece Ancient Greece Timeline Definition History
Classical Greek Society Article Khan Academy
The Greek Polis Article Classical Greece Khan Academy
The Greek Polis Article Classical Greece Khan Academy

Creating Athens Article For Travellers Odyssey Travellers Odyssey Traveller

Chapter 9 Amicitia And The Politics Of Friendship In Valerius Maximus In Reading By Example Valerius Maximus And The Historiography Of Exempla
Chapter 14 Populism And The Logic Of Commodity Fetishism Lukacs S Theory Of Reification And Authoritarian Leaders In Confronting Reification

The Formation Of Greek City States Cairn International Edition

The State Of Content Management 2022 Storyblok

City State Definition History Facts Britannica

Chapter 1 The Premises In Mongol Caucasia

City State Definition History Facts Britannica

City State Definition History Facts Britannica

Camp By A Waterfall At Crosby Manitou State Park In Minnesota State Parks Waterfall Minnesota

Comments
Post a Comment